What's New
Displaying results 1131 - 1140 of 4913
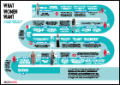
Resource | Infographics,
Girls and women are at the centre of the AIDS response. Factors including age, ethnicity, gender inequities, disability, sexual orientation, profession and socioeconomic status compound to influence girls’ and women’s ability to protect themselves from HIV. Programming efforts must recognize the complexity of the everyday lives of girls and women as they mature and grow and build the response around their needs. Placing the individual—not the virus—at the centre of all our efforts creates the space for inclusion of the diverse opportunities and needs of girls and women and improves HIV outcomes.

Resource | Publications,
Since the 1980s, informal or clandestine sex work in the service or entertainment industry has spread from municipalities to small towns in most areas of China. Despite recognition of the important role of female sex workers in HIV and STD epidemics in China, limited data are available regarding their individual characteristics and social and environmental context of their work. Furthermore, most existing studies on commercial sex in China have been conducted in large cities or tourist attractions. Using data from 454 female sex workers in a rural Chinese county, the current study was designed to explore the individual profile of commercial sex workers and to examine whether the profile and sexual risk behavior differ by where the female sex workers came from and where they work.

Resource | Publications,
The objective is to determine the prevalence of HIV and associated risk factors among female sex workers (FSWs) in border provinces of Vietnam. 911 FSWs in five border provinces of Vietnam (Lai Chau, Quang Tri, Dong Thap, An Giang, and Kien Giang) were enrolled in a cross sectional study.

Resource | Guidelines,
Given the impact of gender inequality on the sexual and reproductive health of women and girls and the health of women and their children, UN Women developed this programming guide that provides practical guidance and tools to understand the influence of gender inequality on sexual, reproductive, maternal, newborn, child and adolescent health (SRMNCAH), and how to effectively integrate gender equality into programming.
The guide serves as an important resource to complement and build on existing guidance and tools to strengthen gender equality efforts to improve health outcomes for women, children, and adolescents.

Resource | Publications,
Indonesia has a large population and is one of the top three countries, after Philippines and Myanmar, to have the highest rate of new HIV infections. Adolescent (15-19 years old) and young (20-24 years old) (AY) key populations (KP), including people who inject drugs (PWID), female sex workers (FSW), males who have sex with males (MSM) and transgender persons (TG), are extremely vulnerable to HIV transmission. However, very little is known about their socio-demographic characteristics, sexual risks, access to services, HIV transmission knowledge and perceived risk and HIV prevalence.

Resource | Publications,
Due to its characteristics, widespread cultivation and use, and diversity of its applications the Cannabis sativa L. plant directly pertains to at least 62 of the 169 targets found in 15 out of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Surprisingly, this plant affects the SDGs both positively and negatively.
This report explains how the “hemp-issues” of Cannabis sativa L. (non psychoactivity-related uses) can contribute to meeting Goals 1, 2, 7, 9, 11, 12, 13 and 15, but also why reforming the current repressive, prohibitive, and marginalizing policies relating to “marijuana-issues” (psychoactivity-related uses of Cannabis sativa L.) is indispensable to meet Goals 3, 4, 5, 8, 10, 13, 16 and 17.

Resource | Publications,
World health statistics 2019 summarizes recent trends and levels in life expectancy and causes of death and reports on the health and health-related Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and associated targets. It then summarizes the major findings, including the availability of underlying data for monitoring progress towards the health-related SDGs (Section 9), and concludes by briefly discussing the implications for health policy and the planning of programmes. Annex 1 provides regional level statistics, Annex 2 presents country-level statistics for selected health-related SDG indicators and Annex 3 summarizes WHO regional groupings.

Resource | Publications,
In November 2017, 117 national delegations adopted the Moscow Declaration to End TB at the first WHO Global Ministerial Conference on Ending TB: A Multisectoral Response. They committed to “supporting the development of a multisectoral accountability framework” to accelerate progress to end TB. They called on WHO to develop the framework, working in close cooperation with relevant partners.
At the 71st World Health Assembly (WHA) in May 2018, Member States welcomed the WHO draft multisectoral accountability framework (hereafter referred to as the MAF-TB). The WHA also requested the Director-General to continue to develop the MAF-TB, in consultation with Member States, and working in close collaboration with partners, as well as to provide technical support for national adaptation and use of the MAF-TB.

Resource | Publications,
WHO is accountable for reporting back to the World Health Assembly on progress in implementing the Global health sector strategies on HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections based on data received from countries. This report assesses the mid-term progress in 2019 in implementing these global health sector strategies from 2016 to 2021.
The timeliness and availability of the data across the three diseases is limited, being for 2016 or 2017 in most cases. Key data, including 2018 impact data on incidence and mortality, were not available for this report, making it difficult to assess and validate overall trends since the launch of the strategies in 2016.






